Allergic Rhinitis, Asthma, COPD, Eczema, Food Allergies, Drug Allergies, Hives, Angioedema, Occupational, Premature or Other Lung Diseases and Sleep Disorders
Attention: Are you constantly dealing with the symptoms of allergies and respiratory conditions?
Interest: Our comprehensive range of treatments and solutions can help you find relief from allergic rhinitis, asthma, COPD, eczema, food allergies, drug allergies, hives, angioedema, occupational, premature, and other lung diseases & Sleep Disorders. No matter your suffering, we have the expertise and resources to address your needs.
Desire: Imagine breathing freely and living without the constant discomfort of allergies and respiratory issues. With our proven treatments and personalized approach, you can regain control of your health and enjoy a better quality of life.
Action: Don't suffer in silence any longer. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and start your journey toward a healthier, allergy-free life.
When to see a doctor
Seek emergency treatment
Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening. Work with your doctor to determine what to do when your signs and symptoms worsen — and when you need emergency treatment. Signs of an asthma emergency include:
Rapid worsening of shortness of breath or wheezing
No improvement even after using a quick-relief inhaler
Shortness of breath when you are doing minimal physical activity
Contact your Doctor at
Colonial Heights
Phone: 804-520-8932
Fax: 804-520-6748
Midlothian
Phone: 804-897-1705
Fax: 804-897-1746
Doctor on Call for Emergencies
Phone: 804-869-8325
E-mail: pedlungallergy@gmail.com
Definition of Allergies
Allergies are common in many individuals, causing discomfort and inconvenience daily. An allergy refers to an exaggerated and adverse immune system reaction toward substances that are typically harmless to most people. These substances, known as allergens, can trigger an immune response in sensitive individuals, leading to various symptoms. Allergies can manifest in multiple forms, including allergic Rhinitis, asthma, eczema, food allergies, drug allergies, hives, angioedema, and occupational-related lung diseases. The severity of allergic reactions can vary from person to person, with some experiencing mild symptoms like itchy skin or sneezing. In contrast, others may endure more severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. Identifying and managing allergies is crucial for maintaining optimal health and quality of life.
Types of Allergies
Allergies are hypersensitive immune responses to substances that are usually harmless. Various types of allergies exist, including allergic Rhinitis, asthma, COPD, eczema, food allergies, drug allergies, hives, angioedema, and occupational, premature, and other lung diseases.
Allergic Rhinitis, also known as hay fever, affects the upper respiratory system and commonly causes sneezing, itching, nasal congestion, and watery eyes.
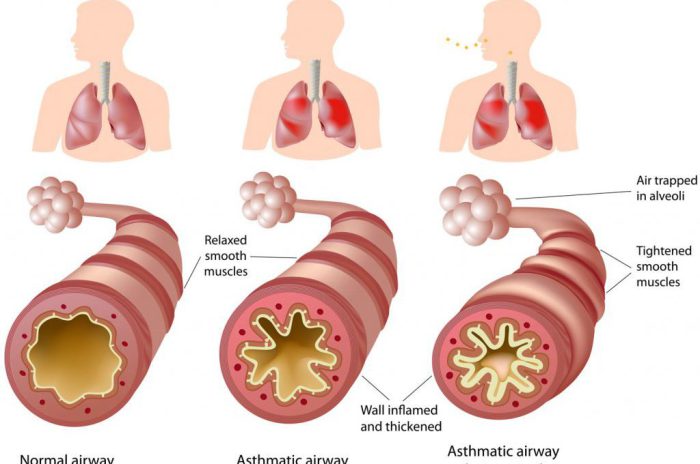
Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the lower respiratory system, causing wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) is a progressive lung disease with chronic bronchitis and emphysema, leading to breathing difficulties.
Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, dry, and red patches on the skin. Food allergies occur when the immune system reacts to certain foods, causing symptoms such as hives, stomach cramps, and diarrhea. Drug allergies involve an allergic reaction to medications, resulting in hives, rash, and sometimes more severe symptoms like anaphylaxis.
Hives, also known as urticaria, are characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin. Angioedema is swelling beneath the skin, typically around the eyes and lips. Occupational lung diseases result from exposure to harmful substances at work, leading to respiratory problems.
Diagnosing allergies involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, skin testing, and blood tests. Treatment options include medication, allergen avoidance, immunotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Preventive measures such as reducing exposure to allergens, maintaining good indoor air quality, and proper hygiene practices can also help manage allergies effectively.
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a common allergic reaction that affects the nose. It occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, or certain foods. Many people experience sneezing, nasal congestion, runny nose, itchy or watery eyes, itching or irritation in the throat, and coughing. These symptoms can significantly impact the quality of life, causing difficulty in daily activities and interfering with sleep. Allergic Rhinitis can be diagnosed through a detailed medical history, a physical exam, and sometimes, blood tests or skin testing. While the condition is not curable, it can be managed through various treatment options, including avoiding allergens, taking antihistamines, nasal sprays, or decongestants, and undergoing allergen immunotherapy. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential for properly diagnosing, treating, and managing allergic Rhinitis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of occupational lung disease can manifest as a range of respiratory issues, including an abnormal breathing pattern, persistent or recurrent coughing, chest pain, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms are the body's way of indicating that there may be underlying lung damage caused by exposure to harmful substances in the workplace.
An abnormal breathing pattern may present as shallow or rapid breaths, difficulty taking deep breaths, or inability to fully inhale. Persistent coughing may be dry or accompanied by the production of mucus. Chest pain can vary in intensity and may be localized or spread across the chest. Chest tightness can create a sensation of pressure or discomfort that can make breathing even more difficult. Additionally, shortness of breath can cause a feeling of breathlessness or the need to take rapid, shallow breaths.
It is crucial to seek medical attention if these symptoms are present, as they may indicate the presence of occupational lung disease. A healthcare provider can perform a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as chest X-rays or pulmonary function tests. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent further lung damage, improve the overall quality of life, and minimize the risk of complications associated with occupational lung disease.
Diagnosis & Testing
When it comes to diagnosing allergic reactions, several diagnostic tests are commonly used. These tests help healthcare providers determine the allergen causing the reaction and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Here are some of the most common diagnostic tests:
1. Skin prick tests: This involves placing a small amount of allergen extract on the skin and then pricking or scratching the skin's surface. If an allergic reaction occurs, such as redness or swelling at the site, it indicates an allergy to that specific allergen.
2. Serum-specific IgE tests: These blood tests measure the levels of IgE antibodies produced in response to specific allergens. Elevated levels of allergen-specific IgE indicate an allergy to that particular allergen.
3. Complete blood count (CBC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP): These blood tests can help identify if there is an underlying infection or inflammation that may be contributing to allergic symptoms.
4. Thyroid autoantibodies: In some cases, autoimmune diseases can cause allergic-like symptoms. Testing for thyroid autoantibodies can help identify if there is an autoimmune component to the allergies.
5. Skin biopsy: This test involves removing a small skin sample for examination under a microscope to identify any abnormalities or determine the cause of a skin reaction.
6. Serum tryptase and complement levels: Elevated serum tryptase and complement levels can indicate certain allergic disorders, such as hereditary angioedema.
7. Serum protein electrophoresis: This test helps identify any abnormalities in the blood's levels or types of proteins, which can help diagnose certain allergic conditions.
8. Autologous serum skin test (ASST): This test involves injecting a person's blood serum into their skin to identify if their antibodies are causing allergic reactions.
9. Basophil activation test: This test is used to measure the activation of basophil cells in response to allergens, indicating the presence of an allergic reaction.
10. Challenge testing: This involves exposing the person to a suspected allergen in a controlled environment to confirm the presence of an allergy and determine the severity of the reaction.
11. In vitro tests: These lab tests measure various mediators and allergen-specific IgE levels in the blood to assess the immune response to specific allergens.
By utilizing these diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose allergic reactions and develop an effective treatment plan to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for occupational lung diseases primarily involve two approaches: avoidance of allergens and nebulized medication.
The most effective treatment for occupational lung diseases is eliminating or minimizing exposure to allergens-causing symptoms. This can be achieved by modifying work practices, using protective equipment such as masks, and implementing proper ventilation systems. In more severe cases, changing jobs or leaving the occupation may be necessary.
In certain situations where symptoms are severe, nebulized medication may be prescribed. This involves using a nebulizer that converts liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled directly into the lungs. Nebulized cures can provide immediate relief and reduce inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, it is important to note that nebulized medication is typically used for severe cases and does not address the underlying cause of the disease.
When using a nebulizer, it is crucial to follow the instructions provided by a healthcare provider. Generally, this involves assembling and cleaning the nebulizer properly, measuring the prescribed medication dosage, and attaching the nebulizer to a power source. The mist should be inhaled slowly and deeply, holding it for a few seconds before exhaling. Regular maintenance of the nebulizer, including cleaning and replacing parts as instructed, is essential for its effective use.
In conclusion, the treatment options for occupational lung diseases include avoidance of allergens and nebulized medication for severe symptoms. It is crucial to follow a healthcare provider's advice for the correct use of a nebulizer to ensure optimal results.
Risk Factors & Complications
Allergic Rhinitis:
Risk factors for developing allergic Rhinitis include a family history of allergies or asthma, having other allergies or asthma, and a history of atopic dermatitis or eczema. Environmental factors such as exposure to allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain irritants may also contribute to the development of allergic Rhinitis.
Complications of allergic Rhinitis can include sinusitis, ear infections, asthma exacerbations, and decreased quality of life. Chronic untreated allergic Rhinitis can lead to sleep disturbances, fatigue, and impaired cognitive function.
Asthma:
Risk factors for asthma include a family history of allergies or asthma, exposure to tobacco smoke, respiratory infections during early childhood, and living or working in environments with poor air quality or allergens. Premature birth, low birth weight, and a history of respiratory distress syndrome are additional risk factors.
Complications of asthma can range from mild to severe. Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening and may require emergency medical attention. Chronic uncontrolled asthma can result in decreased lung function, frequent respiratory infections, and limitations in physical activity and daily life.
COPD:
Risk factors for developing COPD include long-term exposure to tobacco smoke, secondhand smoke, and other environmental pollutants such as occupational dust and chemicals. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, which is an inherited condition, is also a risk factor for the development of COPD.
Complications of COPD can include frequent respiratory infections, pulmonary hypertension, heart problems, and decreased quality of life. Severe COPD can lead to respiratory failure and the need for supplemental oxygen therapy.
Eczema:
Risk factors for eczema (atopic dermatitis) include a family history of allergies or eczema, a history of other allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever, and a weakened immune system. Environmental factors such as exposure to cold, dry climates or harsh chemicals can also trigger or worsen eczema symptoms.
Complications of eczema can include skin infections, chronic itching and scratching leading to scarring or thickening of the skin, sleep disturbances, and impaired quality of life. People with severe eczema may also be at a higher risk of developing other allergic conditions or asthma.
Food Allergies:
Risk factors for food allergies include having other allergic conditions like eczema or asthma, a family history of allergies or asthma, and early exposure to certain allergenic foods. Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions or other food allergies are also at an increased risk.
Complications of food allergies can range from mild to severe, with the potential for anaphylaxis being the most severe complication. Other complications can include gastrointestinal symptoms, skin reactions (hives, itching), and respiratory symptoms like wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Drug Allergies:
Risk factors for drug allergies include a personal or family history of drug allergies, as some drug allergies may have a genetic component. Certain medications, such as antibiotics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may increase the risk of developing an allergic reaction to drugs.
Complications of drug allergies can range from mild to severe, with the potential for anaphylaxis being the most severe complication. Symptoms can include hives, itching, rash, swelling, and in extreme cases, difficulty breathing and a drop in blood pressure.
Hives & Angioedema:
Risk factors for hives and angioedema include a family history of the condition, other allergic conditions, exposure to allergens or irritants, infections, and certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibiotics.
Complications of hives and angioedema can include swelling of the throat or tongue, which can lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing. In severe cases, anaphylaxis can occur, which is a life-threatening emergency.
Occupational Related Lung Diseases:
Risk factors for occupational lung diseases include exposure to specific substances in the workplace, such as asbestos, silica, coal dust, or chemical fumes. Lack of proper safety measures and protective equipment can also increase the risk of developing occupational lung diseases.
Complications of occupational lung diseases can include chronic respiratory symptoms, decreased lung function, respiratory infections, and in severe cases, respiratory failure or the development of other chronic lung diseases.
Premature and Other Lung Diseases:
Risk factors for premature birth and other lung diseases include premature birth, low birth weight, and respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Other risk factors for lung diseases have a history of respiratory infections, exposure to environmental pollutants, tobacco smoke, or secondhand smoke.
Complications of premature birth and other lung diseases can include an increased risk of respiratory infections, chronic lung diseases like bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and long-term respiratory and developmental problems. These conditions can impact the quality of life and require ongoing medical care and treatment.
Quality of Life Considerations
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Several factors can influence the overall well-being and daily activities of individuals with COPD.
Firstly, COPD symptoms such as breathlessness, coughing, and fatigue can make it challenging for individuals to perform routine tasks and engage in physical activities. These symptoms can persist into early adulthood and limit their ability to participate in social events, hobbies, and even simple things like walking or climbing stairs. The constant feeling of breathlessness and decreased physical endurance can reduce the overall quality of life.
Secondly, COPD can affect mental health and emotional well-being. The stress and anxiety related to living with a chronic illness and the limitations imposed by the disease can lead to depression and a decreased sense of self-worth. Social isolation and feelings of frustration or helplessness are also common in individuals with COPD.
However, there are lifestyle changes that can help alleviate COPD symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition. Quitting smoking is crucial, as smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Avoiding secondhand smoke and chemical fumes is vital to protect the lungs from further damage. A healthy eating plan can help maintain overall health and reduce complications associated with COPD. Lastly, discussing safe levels of exercise with a healthcare provider and incorporating regular physical activity into the daily routine can improve lung function and provide relief.
In conclusion, the symptoms of COPD can persist into early adulthood and significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. However, by implementing, individuals with COPD can alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life by implementing lifestyle changes such as smoking cessation, avoiding environmental triggers, adopting a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise.
About Us
We put great value on personal relationships with our patients. Whether at the reception desk or in the examination room, you'll feel attended to at all times.
Our Range of Services
Here, you can find out about all of the services we provide - from diagnosis to immunotherapy.